Livestock Development Programme

The programme assists small and landless farmers to upgrade livestock quality through cross-breeding by artificial insemination to boost milk productivity by a factor of 6 to 9 times, leading to a threshold increase in household incomes and thereby
an improvement in their poverty status. This intervention promotes sustainability in the following ways - (a) By supplementing farm incomes, it reduces pressure on land, thus promoting long-term sustainability of agriculture; (b) It provides a viable livelihood opportunity, thus promoting financial viability of rural households; and (c) We benefit from the secondary effect
of revitalised agriculture since it leads to a stable production regime.
Initiated in 2004-05 with 23 Cattle Development Centres (CDCs), the number increased to 95 CDCs covering 1,910 villages during 2007-08. |
| Activities |
Up to 2006-07 |
2007-2008 |
Todate |
| No. of CDCs |
77 |
18 |
95 |
| Breed Improvement |
| |
No. of AIs |
94,654 |
80,056 |
174,710 |
| |
No. of crossbred heifers |
14,736 |
20,719 |
35,455 |
| Animal Health Service (No.) |
202,741 |
133,734 |
336,475 |
| |
Milk Procurement |
| |
No. of Societies |
34 |
50 |
84 |
| No. of farmers |
1,358 |
553 |
1,911 |
| Volume (lakh litres) 65 |
657,313 |
892,196 |
1,486,509 |
|
The programme also provides integrated animal husbandry services that include pre and post
natal interventions.
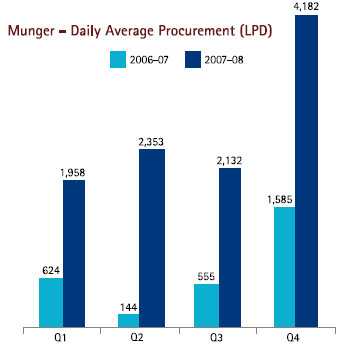
Farmers benefiting from the breed improvement programme also get linked to formal milk
marketing channels to get the best price. This can be assessed from the increase in daily average procurement in Munger, Bihar.
Millennium Development Goal - Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women |
Economic Empowerment of Women
 Promotion of micro-credit groups is only the first step towards the economic empowerment
of women. Mature SHGs are linked with micro-enterprises like incense stick rolling and embroidery to provide diversified sources of income for poor rural households. Moreover, increased incomes
in the hands of women go towards better education and health for their children, thus improving human development in the project areas. Promotion of micro-credit groups is only the first step towards the economic empowerment
of women. Mature SHGs are linked with micro-enterprises like incense stick rolling and embroidery to provide diversified sources of income for poor rural households. Moreover, increased incomes
in the hands of women go towards better education and health for their children, thus improving human development in the project areas.
The total turnover of women-managed micro-enterprises during the year was Rs 69 lakhs, the bulk of which was accounted for by the sale of raw agarbattis and chikkan-kari garments. In addition, the SHGs were able to take bank loans worth Rs 59 lakhs to fund self-employment activities of its women members. |
As a result of the proactive initiatives taken by us jointly with the Director Commissioner, Handicraft (Ministry of Textiles, GoI) 250 chikankari artisans got insured under the Rajiv Gandhi Shilpi Swasthya Bima Yojna and Mediclaim coverage for self and family. |
| Activities |
Up to 2006-07 |
2007-2008 |
Todate |
| Micro-credit programme |
| |
SHGs |
843 |
129 |
972 |
| |
Members |
12,618 |
1,363 |
13,981 |
| Savings (Rs lakhs) |
59.98 |
37.75 |
97.73 |
| Self Employed (No. of women) |
3,917 |
8,844 |
12,761 |
Employed in microenterprises
(No. of women) |
2,229 |
1,097 |
3,326 |
| Skills training (No. of women) |
801 |
118 |
919 |
|

